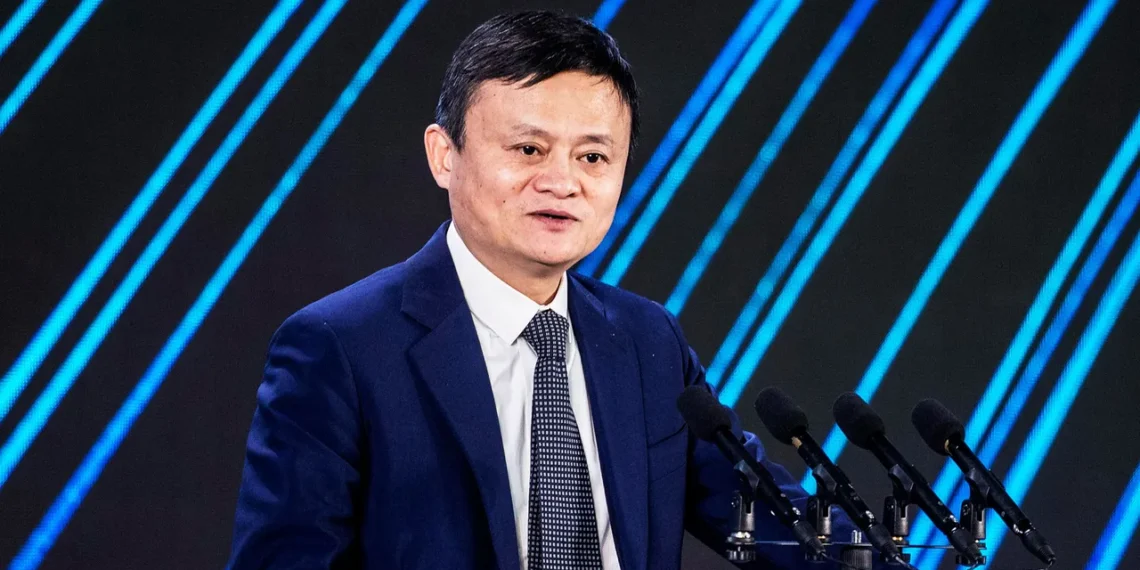
Jack Ma’s life reads like a screenplay penned by fate itself. Picture a young man in Hangzhou, China, failing his college entrance exams—not once, but twice. He applies to 30 different jobs, including one at KFC, and gets rejected from every single one. Despite the mounting “no’s,” an English teacher with zero programming experience stayed curious. His breakthrough didn’t come from luck—it came from unrelenting optimism.
1. A Humble Beginning with a Digital Spark
In 1994, Ma started his first enterprise—a translation agency. It was modest, but it paid his bills and sparked ambition. Then, on a trip to the U.S. in 1995, he typed “China” into a search engine—nothing. That moment ignited a vision: what if the world could find China? Born from that idea came China Pages, an early attempt to connect Chinese businesses online. It wasn’t a massive success, but it showed him the potential of the web. And with that, Alibaba was born.
2. Launching Alibaba from an Apartment, No Tech Needed
In 1999, Ma crowded his small Hangzhou apartment with 17 friends, pitching a daring concept: an online marketplace connecting small Chinese businesses with global buyers. They raised a modest $60,000. With the dot-com bubble bursting, investors were terrified—yet, Ma and his team pressed on. They launched Alibaba.com with purpose: empower SMEs, disrupt the odds, prove them wrong.
3. Turning the Tide with Trust: Taobao and Alipay
The year 2003 marked the real turning point. Alibaba launched Taobao, taking aim at eBay in China—but with their own twist. No listing fees. Tailored user experience. And in 2004 came Alipay—a clever escrow system that held payments until buyers confirmed receipt. These moves didn’t just meet market needs—they rebuilt trust.
Within two years, Taobao overtook eBay’s hold in China. eBay folded and left the Chinese market. With that, Alibaba redefined e-commerce in China—on its own terms.

4. IPO, Platform Expansion, and Global Domination
By 2005, Alibaba was growing fast. It launched Tmall for brand-name sellers and expanded into cloud computing (Alibaba Cloud), logistics, and entertainment. Then in 2014, it executed the largest IPO in global history—raising a staggering $25 billion on the New York Stock Exchange. It solidified not just Alibaba’s future but Jack Ma’s status as a business titan.
Today, Alibaba is a powerhouse: cloud services, global retail, fintech, logistics, and so much more.
5. Culture, Resilience, and Turning Rejection into Momentum
The Numerics are powerful. But it’s the culture and mindset that truly powered Alibaba’s rise. Ma led with values: “customer first, teamwork, integrity.” He pushed boundaries—launching platforms like AliExpress, AliCloud, and diving into entertainment. Each step faced doubts, regulations, or skepticism, yet he kept climbing.
Artwork: “Make your failures your fuel.” That’s Jack Ma: turned rejection into resolve, skepticism into innovation.
6. Global Give-Back: Building a Legacy Beyond Business
Jack Ma didn’t just step down quietly—he shifted gears toward giving. His Jack Ma Foundation became a platform for education, entrepreneurship, rural renewal, and environmental stewardship. Scholarships, school upgrades, disaster relief, young-founder grants—he turned business success into social impact.
Final Act: Why Jack Ma Still Matters
Jack Ma’s journey—18 rejections, zero tech background, building Alibaba from a tiny apartment—reminds us that big ideas don’t need big credentials. They need vision, courage, tenacity, and community. It’s a real-life screenplay that proves: when you stay curious, disrupt norms, and outwork your doubts, you can empower millions and reshape global commerce.